Are you wondering how to do SEO? If so, you’ll love this guide. SEO is an acronym for search engine optimization, which is merely ensuring your site shows up on the first page of Google whenever a user searches for the kind of content or product(s) you offer.
If you’d like to get more traffic from Google, then you must spruce up your SEO.
But, since SEO is a broad subject shrouded in myths and technical mumbo-jumbo, where do you even start?
What to do?
How do you rank on the first page of Google for your keywords and get more organic traffic to your site?

Unlike what many SEO programs will have you believe, SEO is easy; you just need a little elbow grease and some patience. Take it from us; you can learn how to do SEO and rank well for any keyword you desire.
Many other online entrepreneurs just like you do it all the time, and if you stick with white-hat SEO techniques, you needn’t worry about foul Google penalties.
With this preamble, let us dive right in and learn how to optimize your website for free.
0 What Search Engines Look for When Ranking Your Site
We’ve already said SEO is the process of improving the visibility of your website on Google, Yahoo, and Bing among other search engines. With Google dominating the market, we shall optimize for only that search engine in this guide.

A search ranking factor is what Google uses to rank your website, and there are hundreds of these factors. Covering each in details requires an entire post, so we shall keep it short just the way you like it.
Here are a few factors that Google uses to rank your site in no particular order:
- High-quality content – Fluff takes you nowhere in the SEO landscape of today or the future. In the past, you could merely stuff keywords on a page and win high rankings, but you need some high-quality content nowadays.
- Keyword density – While it’s not as effective as it was a while back, keywords are still vital in how Google ranks your website. Don’t overdo it though, or you will catch a penalty.
- Link profile – How is your linking partner? Are you linking to/from spammy sites that tarnish your SEO rankings? Or are you connecting to authority domains in your niche that send you good SEO vibes?
- Image/Video SEO – Now more than ever, you have the golden opportunity to optimize your media content. You can tune images for your site or the videos you upload to YouTube (the second largest search engine only after Google, the parent company)
- Speed – Who is your host? Are you comfy with their performance or do they leave you a lot to desire? Good page speed is a critical Google Ranking Factor because it ushers in fantastic user experience.
For an extended list of Google ranking factors, feel free to check out Brian Dean’s Google’s 200 Ranking Factors: The Complete List.
In the next section, we cover a couple of basic SEO techniques that comprise the bulk of optimizing your site for Google. Let’s begin with On-Page SEO techniques you should invest in right away.
1 On-Page SEO
As you learn how to do SEO, you’ll come across terms such as On-Page and Off-Page SEO. So, what is the difference?
Off-Page SEO represents all the SEO techniques you apply externally with a good example being external linking.
On the other hand, On-Page SEO involves optimizing a web page (or pages) on your site to shine in Google among other search engines.
Below are a couple of things that should concern you as far as On-Page SEO goes.
1.1 Title Tag
The title tag is a vital ingredient in perfecting the SEO formula that works for your site. Why? Because the title tag offers you a unique advantage regarding usability, recognition and search engine indexability.
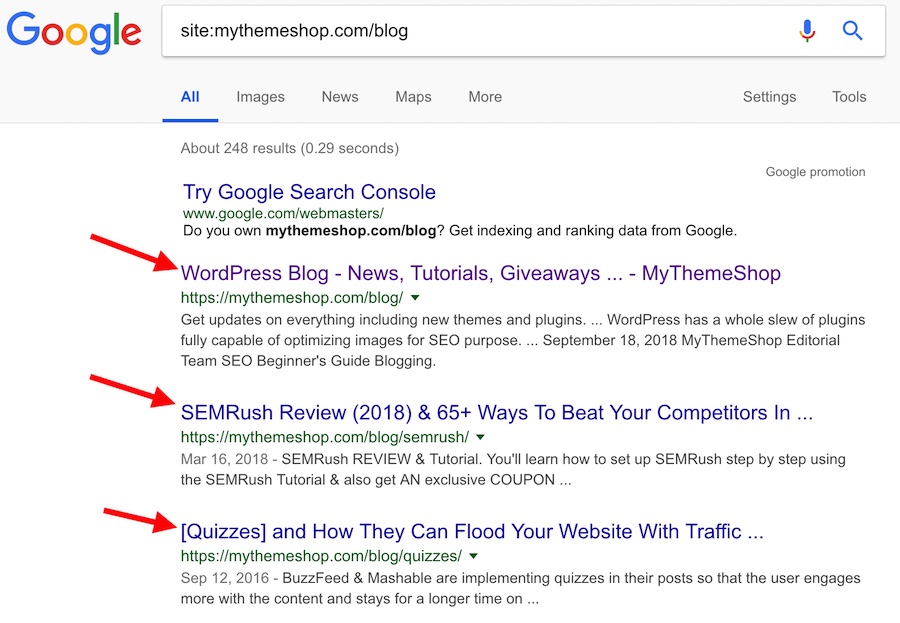
Whenever you search on Google, you get a search engine result page (SERP) that lists clickable titles. These are title tags, and they help Google and readers find your content.
For starters, a title tag gives your page or post a title. You don’t need a degree in rocket science to see just how hard it is to find content without a title. Plus a great title always results in more clicks.
Apart from showing in SERPs, your title appears in your browser alongside your favicon, which boosts usability since any user with multiple tabs open can easily find your content.
That’s not the end of it. Titles look great in social media posts. By default, social networks grab your title tag and some description to create the social post you share. Without a title, your post would be, well, broken, which isn’t how to do SEO.
1.1.1 How To Write a Good SEO Title?
Firstly, strive to keep your titles short; 60 characters or less. Long titles don’t show in full on search results, which might hide essential words. Think of newspaper headlines; short and snappy enough to draw attention.
Secondly, add your keyword in the title, preferably towards the beginning. Readers perform searches using keywords, meaning including one in your page titles boosts your visibility.
Furthermore, Google bolds keywords in search results. Just don’t go overboard with your keywords, stuffing the title with keywords. Nope, that isn’t the way; Google penalizes this as spam and a black-hat SEO trick.
Thirdly, avoid duplicate titles on your site. Each page or post must have a unique title. Remember, we said Google uses titles among other factors to determine the topic of your page. An exclusive title is the best way to go.
At the same time, write your titles for human beings, not search engines. Lest you forget, you are doing all this so you can get more clicks on Google. Yes, we understand you’re learning how to do SEO, but hard and bone-dry titles just won’t cut it.
For an extended overview of the title tag and how it affects your SEO, feel free to read What is a Title Tag by Moz.com.
1.2 Meta Description
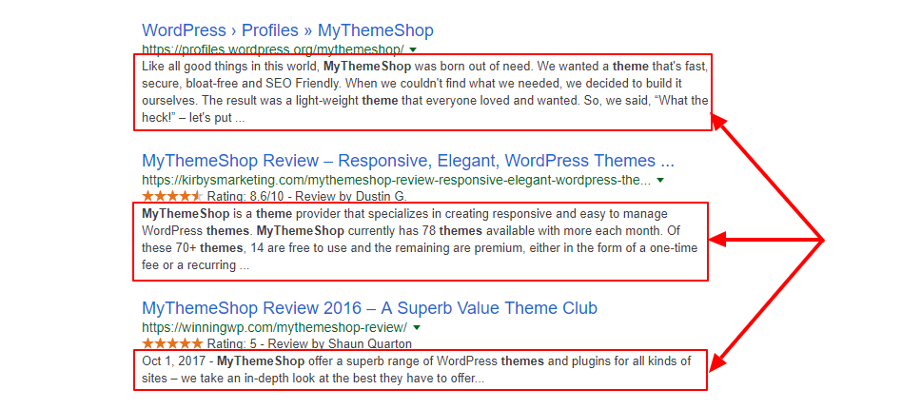
A summary of your page that you write for search engines is a meta description. We say this because meta descriptions do not show alongside your post/page on your site.
For best results, it’s advisable to keep things short and include your main keyword in your meta description.
All the same, Google does not factor meta descriptions into SEO ranking algorithms. Still, the search engine shows your meta description alongside the clickable title tags in SERPs (see image above).
If you write a fantastic meta description, it will garner you more clicks from Google. If these people click-through to your site and find your content useful, it will reflect well on your SEO profile.
A meta description is shorter or equal to 160 characters, meaning you have to spur well in this area. Regardless, you can write meta descriptions like a pro in no time – you just need a little bit of exercise.
As a WordPress user, you probably know of Rank Math SEO, one of the best WordPress SEO plugins in the industry. Well, if it does nothing else for you, this plugin allows you to write helpful meta descriptions inside the post editor.
You should write your meta description like advertising copy, but hold your horses mate. Jamming keywords into your meta description is overkill, and comes across as spammy, which does the opposite of what you intend.
Angle for enticing but not pushy. Remember your one keyword keeping in mind how searchers consume the results in Google. Then make a promise. One that you fulfill within the post. Hook them long before they’re on your site but don’t deceive.
Most webmasters still learning how to do SEO usually forget one crucial thing: writing meta descriptions for all of their pages and posts. Don’t make the same mistake, but make sure the meta description moves your visitors to click through to your site.
According to an article about How to Write an Effective Meta Description written by Ramesh Ranjan for HubSpot, a meta description “…is one of your last hopes on search engine results pages (SERPs) to attract a searcher to come to your site.”
1.3 Internal Links

Without links, the internet itself would cease to exist. Creating relevant links in your content is one of the best search engine optimization tips you’ll learn here today. Why? Google and readers use links to find your content.
But you might be tempted to think linking internally merely means adding a link to another page/post on your site. While this is encouraged, there is more to internal linking than meets the eye.
A good internal linking strategy can help you establish content hierarchy, boost the authority/link value of essential pages and help Google understand the relevance of your content.
Moreover, internal links help Google to determine the architecture of your site and discover more related content. Links are so efficient, which made the bad guys game links like madmen in the past until Google caught up with them.
Your homepage has the most link value, considering it gets the most backlinks. You can use internal linking to pass this link juice to other pages on your site, directing the most juice to popular pages of course.
That said, a correctly built navigation is a must-have. That, and a sitemap as well. We say this because you can have the best of content that Google never finds because there are no links to it from your homepage.
In essence, you should ensure there are a few steps between your homepage and any other page. SEO experts recommend comparing your site to a pyramid, with the tip being your homepage.
Link value will then trickle down from the homepage to other pages under it. Due to its success, this structure is conventional in high-performing websites such as eBay, Amazon and so on.
With the right linking structure, Google can find more of your content straight from your homepage. Without wasting a second, link to your most popular pages and posts directly from the homepage, and you’ll grasp what we mean.
The success of internal linking bore many related posts plugins, widgets, and the works. Since it is so simple to implement, always add “related posts” widgets to your blog posts to get Google and readers to more of your content.
If you add a WordPress post to a category, it automatically creates a link to that group, where Google and readers can find more of the same content. On top of that, you can add links to your tags because, why not?
To point you in the right direction, we found The Seven Commandments of Internal Linking that Will Improve Content Marketing SEO and Internal Linking SEO – What, Why and How?
1.4 Now, The Warnings
Google search spiders follow about 100 links on any page, so avoid adding thousands of links on any single page. It’s horrifying just thinking about it, but adding an excessive number of links means your internal pages will get little if any PageRank. However, this is only a recommendation by Google.
Another thing, don’t shroud your links in JavaScript since doing so gives Google the perfect excuse to ignore or even punish you. Stick to standard HTML links, or you will burn.
Anchor texts are great, but they suck if they aren’t natural. So avoid stuffing keywords in your anchor texts. The anchor text should feel natural within your blog post. The preceding internal link is an excellent example of a suitable anchor text.
Then we have the rel=”nofollow” tag you can add to your links to discourage Google spiders from crawling unimportant links. It works, but you should consider adding fewer links as opposed to “no-following” them.
2 Optimize Images

We all know a picture is worth a thousand words, and a barrage of text is a burden to read. You need images to spice things up, which results in better aesthetics and – wait for it – SEO!
To point you in the right direction, you want to avoid adding images for the sake of adding. You need the proper photos; clean pictures that are relevant and valuable to your page.
You can take professional photos of your team, face, office or product.
The best image is one that’s in tune with the content surrounding it. Remember, your readers can see the pictures, even if Google won’t. If the image rubs the reader the wrong way, it hurts your SEO since other signals (such as higher bounce rates) are triggered.
Once you have the perfect image, begin by optimizing the size in dimensions (length and width) and bytes. For instance, if you need a 700px x 300px image, upload a file with that width and height and not a pixel more.
Cut out extra data such as EXIF or metadata that makes your images heavy. Aim for less than 100Kb for best results. Image size has everything to do with page load speed. The lighter the photos, the better.
With your images cut to size, it’s time to name them appropriately. If your picture shows “how to do SEO,” you can name it how-to-do-seo.jpg. Doing this offers you the opportunity to add your SEO keyword to your titles.
Additionally, ensure your images are responsive to avoid breaking the user experience on mobile devices. Bad user experience leads to higher bounce rates, which is nasty for your SEO. Good thing the latest version of WordPress comes with this feature.
Next, use the alt attribute to describe your images. The alt text (alternative text) is displayed in case your image fails to load for one reason or another.
Make sure your alt text contains your SEO keyword and describes the image accurately. Why? Because the browser, screen readers, and Google search spiders use alt text to “see” your pictures.
Alt text helps you to offer better user experience and put your SEO keywords out there.
Remember also; social media sites pick an image from your post when you hit the share button meaning the right image will lead to more shares and better SEO ranking, which translate to more traffic.
Lastly, quality overcomes quantity as far as image and SEO go. Get amazing images (i.e., photos, infographics, graphs, animated GIF, etc.), but don’t kill your pages with an excessive number of images.
You can edit your images using a tool such as Adobe Photoshop, GIMP or Pixlr.
There is more to say about optimizing images for SEO, which would require a lengthy post. To save you the trouble of looking around, here is The Ultimate Guide to Image Optimization for WordPress by Marko Prelec.
3 URL
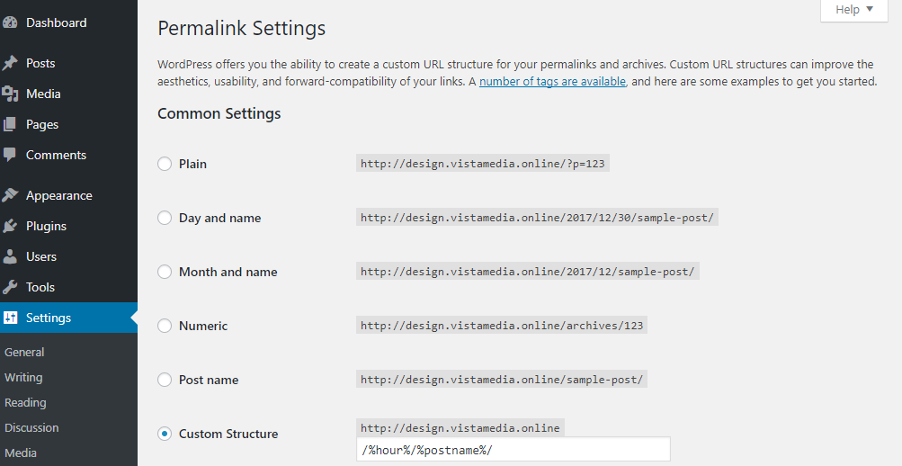
Your URLs play a role in SEO, but the URL itself is a minor ranking factor. Including your keyword in the URL can boost your ability to rank any given page, but that is just about it.
URL, short for universal resource locator, is merely the address of a page/post on your site. For example, https://mythemeshop.com/blog/ is the URL of our blog page.
While it is not much of a ranking factor, good URL structure is great for usability, which is fantastic for your overall SEO campaign. That said, the more readable the URL is to human beings, the better.
There are well-written URLs that will entice readers to click-through to your site, but other URLs will have your visitors running for the hills. Note that shorter URLs that contain your keyword work like magic.
Moreover, canonicalize URLs that point to the same page. If page X and page Y provide the same kind of information, you can canonicalize them by redirecting one to the other. Alternatively, you can use the rel=canonical tag.
Avoid using dynamic parameters in your URLs. For instance, yourdomain.com/page/redirect.aspx?type=banner&id=2 is awkward compared to yourdomain.com/page/redirect. One is more comfortable to share and recall.
WordPress ships with a fantastic permalinks feature (go to Settings -> Permalinks in your WordPress admin) that helps you to create impressive URLs automatically. Alternatively, feel free to use a plugin such as URL Shortener by MyThemeShop to generate and track pretty URLs on your WordPress site.
Endeavor to match your URLs to your titles, but remember to keep things short. For instance, if your post is “How to Do SEO: Optimizing Your Site for Google,” your URL could be yourdomain.com/how-to-do-seo or yourdomain.com/optimizing-your-site-for-google.
In a nutshell, write short human-readable URLs that include one keyword only. Stuffing keywords in your URLs will likely result in a lower click-through rate because – come on – who can’t see all that spam?
Let’s move on swiftly.
4 Schema
What is schema as far as SEO is concerned? Well, Schema is a set of tags that you can use to control how your page appears in SERPs. What does that even mean?
A typical search result in Google usually looks this:
A search result with Schema looks like this:
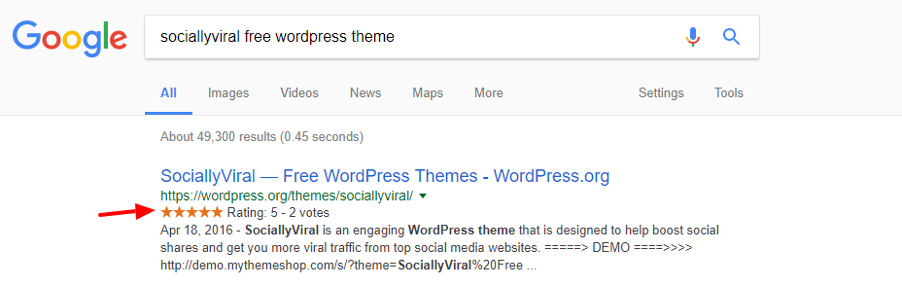
Can you spot the difference? Which one looks better? Well, the second search result has a publication date and a star rating, which adds more weight to the result compared to the first scenario.
By any means, your web visitor is more likely to click on search results with Schema rich snippets compared to results without these tags. You probably prefer results with Schema tags as well.
Does Schema improve your SEO? Yes, it improves your SEO indirectly since more click-throughs usually come with better rankings especially if the page is relevant, useful and shareable.
Adding Schema Structured data to your site is as simple as A, B, C. You can use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper. If you have a WordPress site, you can use plugins such as Schema and All In One Schema Rich Snippets among others.
If you need a hand setting up Schema on your WordPress site, here’s a handy guide by Colin Newcomer: How To Add Schema And Rich Snippets In WordPress.
5 Open Graph
Open Graph is a web technology that allows you to integrate your website with Facebook’s user data. This way, you can choose what shows on Facebook whenever a user shares your content.
This tech comes with a couple of meta tags such as:
- og:title, which allows you to specify the title of your page
- og:image to define the image to use when you share your page
- og:description for that all-important summary of your page
- og:type, which allows you to specify the type of content e.g., article, album, music, video, etc
- og:locale to set the geographical location (defaults to en_US unless you use a different language)
- og:url, which is the canonical URL of your page or post
- And many more.
If you need a plugin, use Rank Math SEO to set up your Open Graph meta tags and check if everything is working right using the Facebook Debugger tool.
And here is How to Install and Setup Rank Math SEO Plugin like a pro.
Now that we have some On-Page SEO techniques with which to work, let’s move on to the next part of search engine optimization, keyword research.
6 Keyword Research

Keyword research is everything in SEO. It is one of the first things you do as far as optimizing your site for Google goes.
What is in it for you?
Search engine visitors usually use a query to find content online. This query could be a full question, phrase or simple word.
If you need a WordPress theme, for instance, you might use “Which is the best WordPress theme?”, “premium WordPress theme” or “WordPress theme” among many other variations.
Google then retrieves the most relevant content to match the query. From our example above, you can see “WordPress theme” is the most effective keyword in the three search queries.
If you publish high-quality content around the keyword “WordPress theme” and follow all other SEO guidelines, you’re likely to appear on the first page of Google for search queries that contain the said keyword.
Google won’t show results for hair shampoo if you’re after WordPress themes, which brings us back to the importance of keyword research.
Firstly, to reach your target audience, you must have an idea of the keywords and phrases they use to find your content (or the content your competition publishes).
Armed with the right keywords, you can write content that ranks highly for the keywords, in turn, increasing the volume of traffic from Google.
If you’re interested, feel free to read Chelsea Baldwin’s 38 Places to Find the Best Keywords in Your Niche.
That out of the way, here are a couple of things to keep in mind as you do your SEO keyword research.
7 The Long Tail

Long tail keywords are usually more extended and more specific than common keywords. For instance, “premium responsive multi-purpose blog WordPress theme” is longer and more specific than “WordPress theme.”
Why are long tail keywords valuable considering they are usually harder to add to any page? Glad you asked. Long-tail keywords are more comfortable to rank in Google and typically have better conversion rates because – specificity.
It’s easier to rank “premium multipurpose responsive WordPress theme” than “WordPress theme,” since the latter has stricter competition from established brands.
Any person who uses a long-tail keyword to find your website is a more promising prospect than the guy who uses one or two words. A user who searches “premium responsive healthcare WordPress theme” is more likely to engage/convert than the guy looking for “WordPress theme.”
Could this be the reason why more and more people prefer the long-tail keyword over the common keyword? Well, you can target long-tail keywords as well as their shorter counterparts.
Brian Dean of Backlinko shows you more tools and ways to find long-tail keywords in How to Find Long Tail Keywords. Read the guide in your spare time to learn more.
Before we proceed, let’s determine the difference between exact, partial and phrase match as far as keywords are concerned.
7.1 Exact, Partial and Phrase Match
Exact match refers to search results that match the query accurately as entered. If you have an ad for “Lego Blocks Online” that shows in results when the user searches for “Lego blocks online,” that’s an exact match.
You can search exact match keywords by wrapping the keyword in quotation marks. So instead of entering the phrase Lego blocks in Google, you write the words surrounded by quotation marks as shown below:
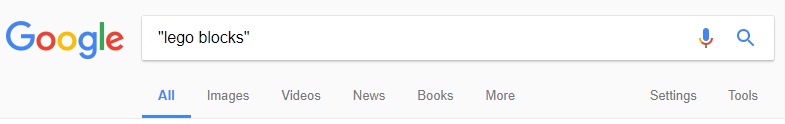
Exact match is a match type that helps you to target your ads to people who search using the exact keyword you’re bidding on in Google AdWords. An exact match keyword results in higher click-through rates.
7.2 Partial Match
Partial Match represents search results that match a part of the search query. In other words, your keyword is among other words in the search query.
For instance, if your long-tail keyword is “responsive WordPress theme,” you can think of results showing “buy premium responsive WordPress theme today” as a partial match.
Partial match keywords might appear in ads that don’t match the search query word for word. If your keyword is “WordPress theme,” using a partial match approach can help you garner traffic from queries such as “buy WordPress theme,” “premium WordPress theme” and other queries that contain your keyword.
7.3 Phrase Match
According to WordStream, a Phrase Match is “…is a keyword matching option whereby Google AdWords matches your ad only against keywords that include a phrase you designate.” Not a word more.
Now, let us get into the thick of it and cover a couple of tools you can use to find long-tail keywords for your SEO campaign.
8 Finding The Long-Tail Keyword
Finding long-tail keywords is easy stuff since all you need is a seed keyword. For instance, we’ve peppered this post with seed keywords such as “WordPress theme” and “Lego blocks.”
You can begin your search on Google. Just head over to Google.com and perform a search using your seed keyword. Next, scroll to the bottom where you see searches related to the seed keyword.
For instance, our “WordPress theme” seed keyword shows the following related searches: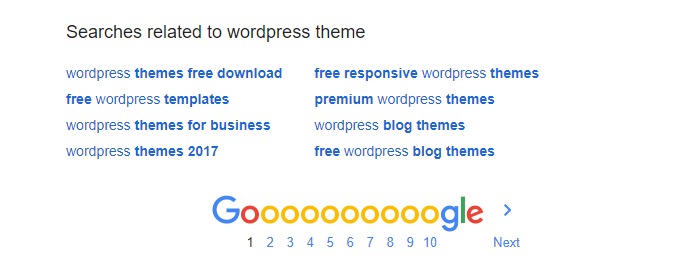
To build a list of long-tail keywords, pick one of the results in the section pictured above and pop it back into Google to generate more related searches.
Alternatively, you can use the LSIGraph tool to generate a list of long-tail keywords related to your primary keywords. It’s free and easy to use.
That out of the way, let’s look at more tools you can use to find keywords ideas.
8.1 Google Keyword Planner
Brought you to by Google AdWords, the Keyword Planner is one of the most popular keyword research tools to ever grace the internet.
Using this tool to generate more keyword ideas is incredibly comfortable we don’t expect you to run into any problems. Just log in to the Keyword Planner.
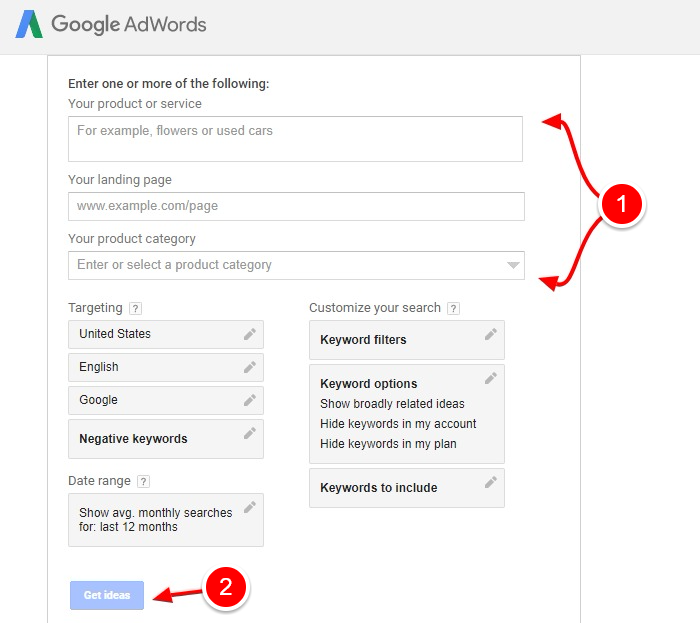
Next, enter your keyword (long-tailor or otherwise) and hit the Get ideas button. Alternatively, you can use your website address or product category to develop more keyword ideas.
The next screen shows you a whole lot of keywords and their different variations:
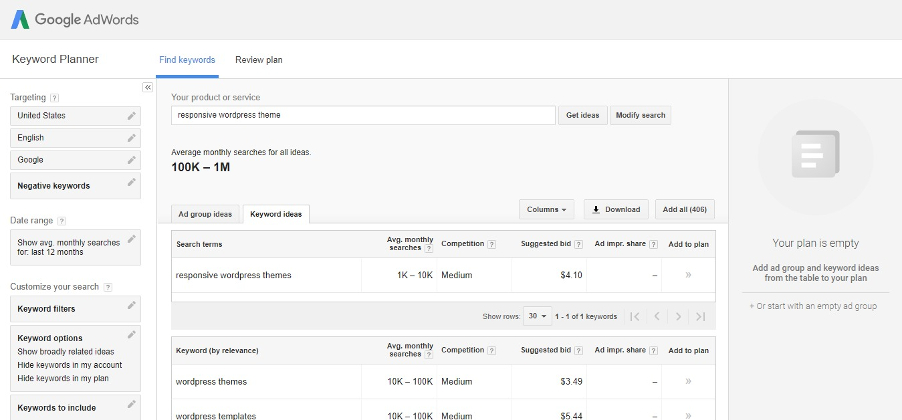
8.2 Ahrefs
Ahrefs Keyword Explorer tool will blow your mind. Unlike Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs Keyword Explorer is a subscription-based tool costing between $99 and $349 bucks per month.
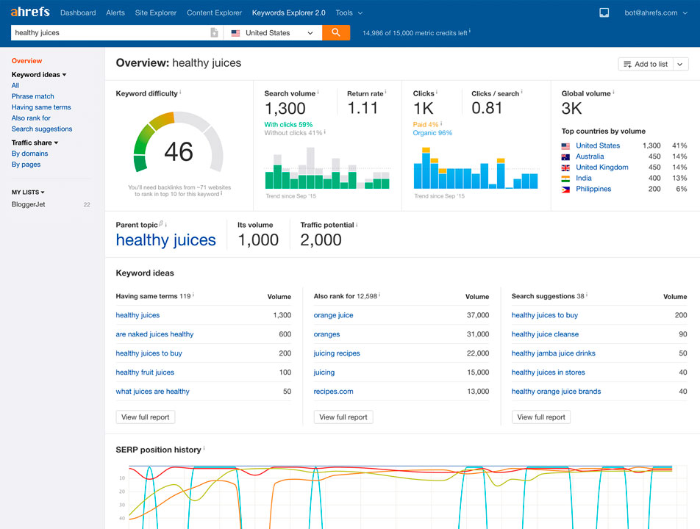
It uses proprietary technology that helps you to take your keyword research to the next level. This tool comes with features such as unlimited keyword suggestions, keyword difficulty score, advanced metrics and much more.
8.3 SEMrush
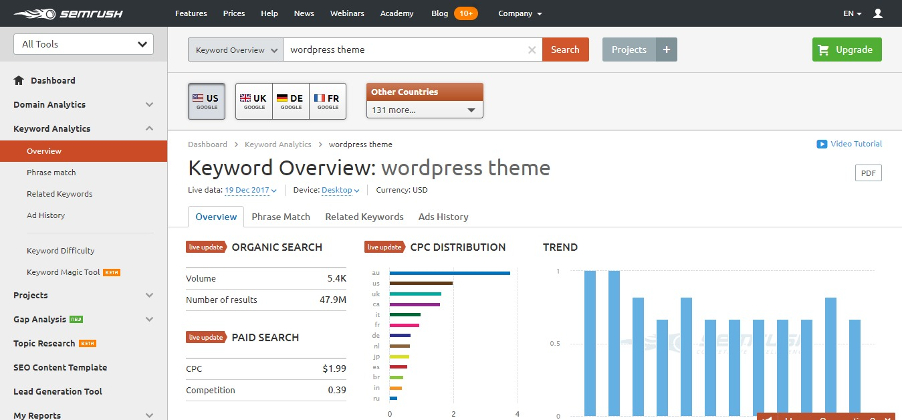
SEMrush is more of an all-in-one marketing toolkit than a keyword tool. It is one of the best search engine optimization services out there.
They offer you a fantastic suite of website optimization features that have endeared SEMrush to big name brands such as eBay, Quora, and Disney among others.
One of their better-known features is the Keyword Research tool. In a simple line, you will have a great time at SEMrush despite the price tag.
8.4 Google Suggestions
Nowadays, whenever you start typing a query in Google, the search engine auto-completes the question with a couple of suggestions.
These suggestions make for fantastic keyword ideas:
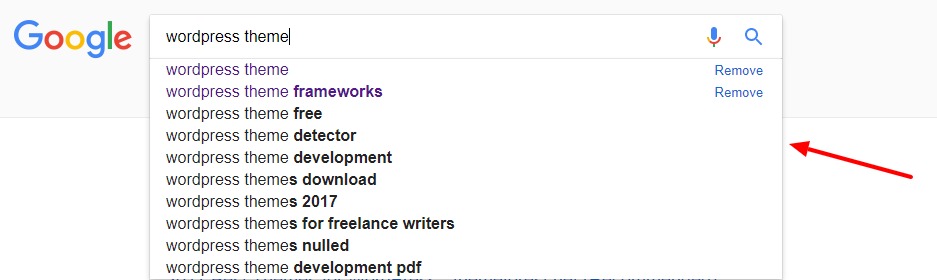
As you can see, there are a couple of keyword research tools at your absolute disposal. With these four recommendations, you can generate keyword ideas like a boss in no time.
Let us move to the final section of optimizing your site for Google – speed optimization.
9 Speed Optimization

There is a need for speed where SEO is concerned. If you’re looking to rank well, you need a speedier website. For better rankings, you need faster pages.
Why is speed important in website optimization? For starters, page speed is a ranking factor with Google favoring faster pages over slower pages.
The reason behind this is simple.
A slow website never offers good user experience, because who wants to stick around waiting for a web page to load? You hate slow loading pages, don’t you? We hate them too.
If you offer nightmarish user experience, you shouldn’t be surprised if you register bounce rates that are through the roof. Again, this is because no one is willing to wait for slow pages, so they hit the back button or exit your site altogether.
Speed is particularly important in this era of mobile search, which is why Google is spearheading the AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) project.
If you have a laggard website, it’s time to put your house in order with the following tips.
9.1 Compress Images
While we’ve mentioned this, optimizing your images has a direct impact on your page speeds. The larger the image file, the longer it will take to load, which is just nasty.
High-resolution images look incredible, but when they slow down your site, we bet you don’t think they are incredible then. Best is to upload optimized images that are no larger than they need to be.
You can compress your images using Photoshop or GIMP, but if that’s not an option, you can go with an online service such as Kraken or a plugin such as WP Smush among others.
In our opinion, you can achieve the best results by uploading images that are already optimized, instead of uploading first and optimizing later on.
To learn more about compressing images and improving your page load speeds in general, read How To Make Your Website Load Faster Using W3 Total Cache Plugin?
9.2 Host Images Separately

You can lighten the load on your web server by serving images separately from a third-party network. While we don’t recommend this for essential SEO images, you can use a site such as Flickr and Dropbox to serve your other decorative images.
For instance, if you took hundreds of high-res photographs at an event or while traveling, you can host these on a third-party site and embed the album on your site instead of uploading each image to your web server.
If you’re uncertain how hosting images separately improve page speed, here is a tip. When you host images on a separate server, they load in parallel to other elements on your site resulting in faster page speeds.
However, if your images and your site live on the same server, the images are loaded in sequence, which results in slower load times.
Check out WordPress CDN Integration with CDN Enabler by Keycdn to learn how to serve your images separately using Keycdn, one of the content delivery networks we mention later in this post.
9.3 Load Fewer External Objects

Loading many external objects slows down your pages. For instance, research shows that loading one stylesheet of 50KB is two times faster than loading five stylesheets of 10KB each.
Why? Many requests for small files creates a bottleneck in the upstream for many internet users. Additionally, while some browsers can load up to four images simultaneously, these objects load one after the other.
In some setups, your images might load after the external objects have loaded, which slows down your pages, more so if you are requesting lots of these objects.
9.4 Unconditional Caching
Caching is one of the best and easiest ways of speeding up things on your site. There are many types of caches where WordPress sites are concerned, and you can leverage each to boost your page load speeds tenfold.
If you need help caching your WordPress site, we recommend How To Make Your Website Load Faster Using W3 Total Cache Plugin.
9.5 Compress and Minimize Code
You can improve the speed of your pages further by compressing and minimizing code. How do you squeeze and reduce your codebase? Read on.
Compressing pages on your site can lead to a 70% decrease in page load times. The best part is you can enable compression with a few clicks using a plugin such as Check and Enable GZIP Compression.
What about minimizing code? Well, reducing your source code, i.e., HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, involves eliminating blank spaces, formatting, commas, code comments, unused code and other useless characters.
Google recommends:
- HTMLMinifier to minify HTML
- CSSNano or CSSO to minify CSS and
- UglifyJS to minimize JavaScript
Additionally, you can integrate Google’s PageSpeed Module with your Apache or Nginx server to optimize your site automatically. How sweet?
9.6 CDN

CDN is short for Content Delivery Network, which is merely a service that accelerates your content. In simpler words, it is a distributed system of proxy servers and data centers across the globe, with each data center carrying a copy of your site.
Whenever a user loads your website, the content loads from a server nearest to their geographical location. For example, if your origin server is in the US, a user in the UK might experience slower speeds than a user closest to the origin server.
However, if you use a CDN, you can serve the content from a server in the UK, significantly increasing the page speeds. Setting up a CDN is the stuff of fourth graders; anyone can do it.
Popular CDNs include CloudFlare, Stackpath (formerly known as MaxCDN) and Keycdn among others.
9.7 Related Reading
We can’t possibly cover all there is to SEO in a single post. For this very reason, we have hand-picked some impressive guides on every little thing you’d like to learn about SEO:
10 Final Words
Optimizing your site to rank favorably in Google is a demanding task, albeit doable. The best course of action is to tackle each SEO technique individually. Finish one and move on to the next one.
In summary, do your keyword research beforehand, learn how to write SEO content and follow these website optimization tips. At the end of the day, offering excellent user experience on your site is vital to the success of your SEO strategy.
Have learned how to do SEO? Did we leave something out? Do you have a question or comment? Please wow us with your genius in the comment section below!




