Whenever you move around the internet, accessing different websites, you leave a digital footprint.
Webmasters use JavaScript applications, cookies, or other technology to record, keep track, or measure the number of visits and unique visitors to the website.
The captured data is then used to understand the customer’s website experience and optimize the website without actively disclosing personal details.
While most users rely on history and cookie clearing to protect their privacy or put an end to data collection, very few are actually aware that their own operation systems capture their browsing behaviors.
A good example is the DNS cache, which stores the IP addresses for every website you visit. This allows your browser to find this information quickly, thus allowing faster connections.
However, there are reasons why you may need to flush your DNS cache regularly. In this article, we will look at the reasons as well as how to flush your DNS cache.
But before we dive into the details, let’s get an overview of what DNS cache is.
What is DNS cache and how does it work?
The Domain Name Server (DNS) cache, sometimes referred to as DNS resolver cache is a database that’s temporarily maintained by your computer’s operating system.
The database stores all records of the recently visited websites, including their IP addresses and other internet domains.
Simply stated, the DNS cache is like your computer’s phonebook. With a phonebook, you do not need to remember everyone’s contact information.
DNS works in a similar way, in that it stores DNS information of every website’s IP address you visit or attempt to visit.
The DNS information stored allows your browser to find the website quickly. What this means is that, once you enter the domain name of the website you are looking for, your browser will first look for the DNS information in the DNS cache. This information will then be used to visit the website.
However, if the DNS information is missing in the local DNS cache, your browser will be prompted to collect it from other DNS servers.
The principle behind DNS technology is to ensure that your browser takes the shortest route when locating any website on the internet.
Why is it important to flush your DNS cache?
There are a number of reasons why you may be prompted to flush your DNS cache. Here are some of the reasons.
- Speed up DNS propagation: But what is DNS propagation, you might ask? This is the time frame required by DNS servers across the globe to update cached information for a domain name after making any changes to your domain or when you are moving your site to a new host. It is determined by the changed Time to Live (TTL) value of DNS records. Sometimes the DNS information can take as much as 72 hours to update completely. As such, you will most likely get a “not found error” or end up visiting the old website. Fortunately, you can speed up the process by flushing your local DNS cache.
- Security: Anyone with access to your computer can without your knowledge access the DNS cache and predict your browsing history. Furthermore, DNS cache files are very vulnerable to DNS cache poisoning (also known as DNS spoofing). DNS spoofing has been used by hackers severely to steal user’s sensitive information like login credentials or to redirect traffic to a fraudulent website.
- Solve connection problems: Sometimes your computer may connect to a Wi-Fi, but not you are still unable to connect to the internet with your browser. This issue normally arises when your DNS cache is outdated or corrupt. Clearing the DNS cache can resolve this issue.
How to Clear Local DNS Cache?
Flushing your DNS cache is dependent on the operating system you are using. In this tutorial, we’ll look at how to flush DNS cache on Windows, Mac, and Linux systems.
How to flush DNS cache on Windows XP, 7, Vista, 8, and 10?
If you are using any of the above Windows Operating Systems on your computer, follow the steps below to clear DNS cache.
Step 1: Click on Start or press the Windows logo key on your keyboard. Select the command prompt tool. If you are using Windows 8, you might need to type “command prompt” on the search bar.
Step 2: Click on it to launch the command prompt window.
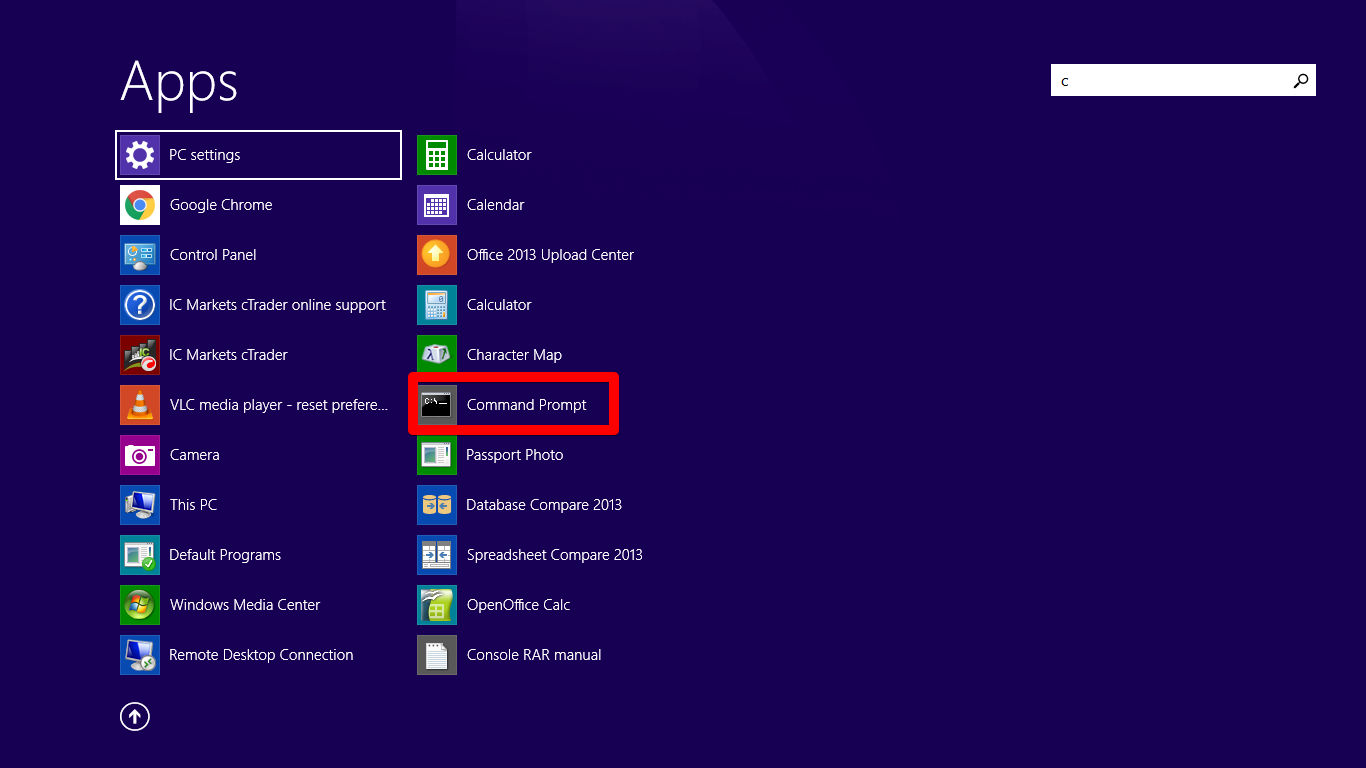
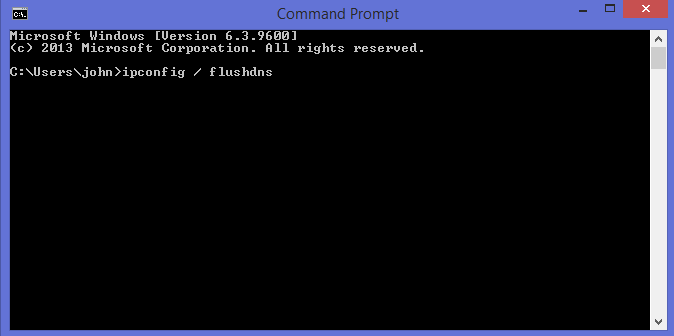
Step 3: Now, you’ll need to type the following command inside the window:
ipconfig /flushdns
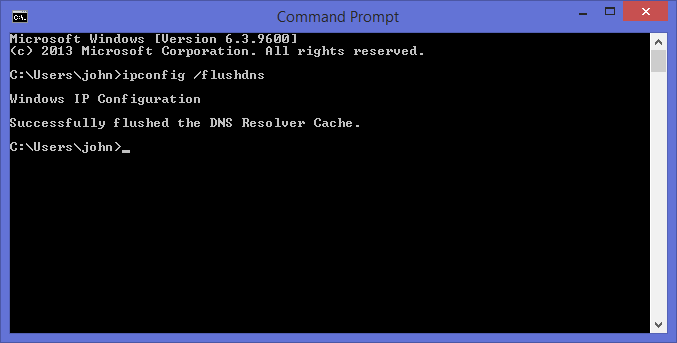
Step 4: Now press Enter to execute the command. This will automatically flush the DNS cache and you’ll be greeted by a “Successfully flushed the DNS resolver cache” message. That’s it!
How to flush local DNS cache in Mac OS?
If you are using a Mac OS computer, follow the following steps.
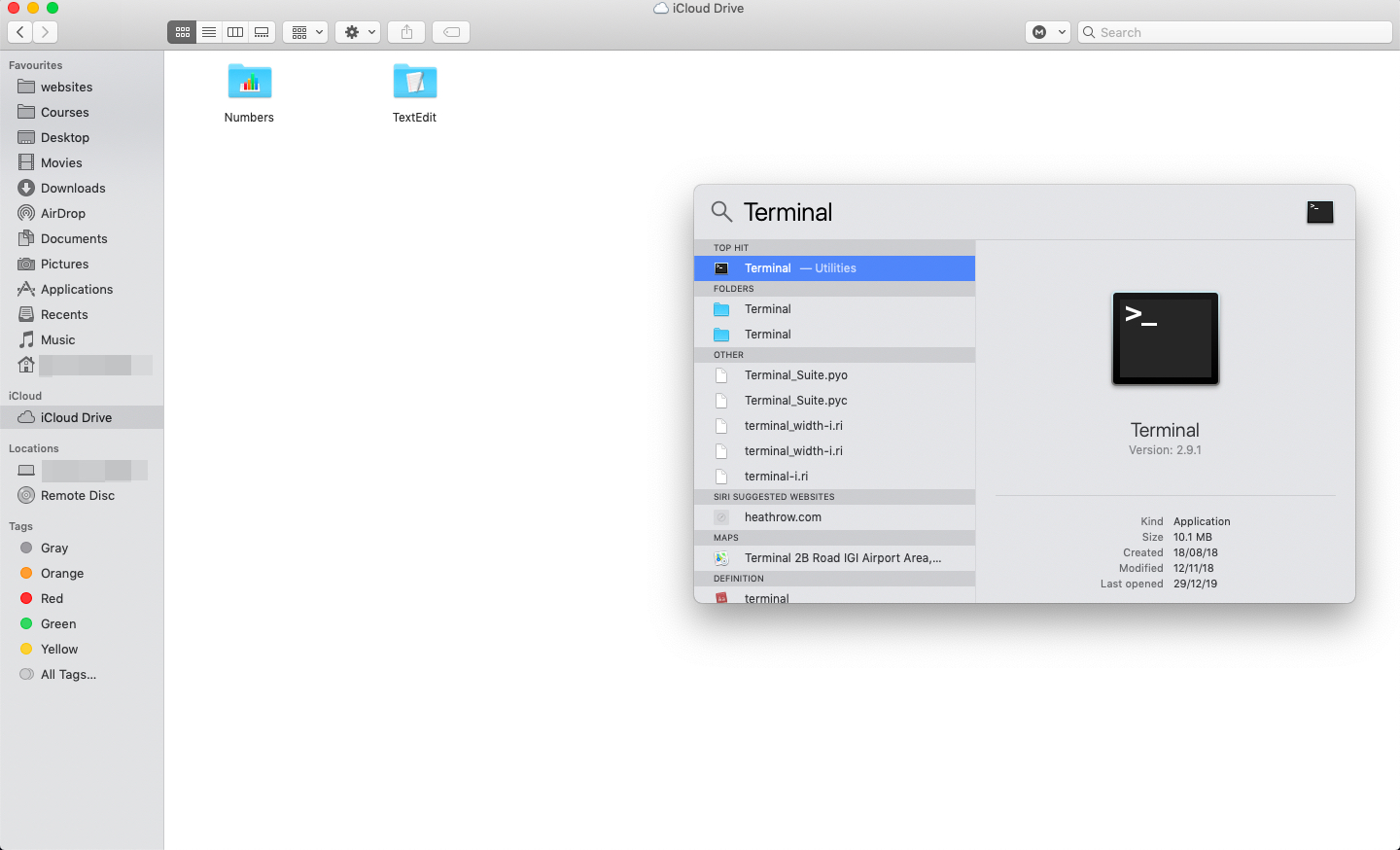
Step 1: Press the Functions key F4. On the Launchpad’s search field, type terminal. Alternatively, you can go to Applications >> Utilities >> Terminal.
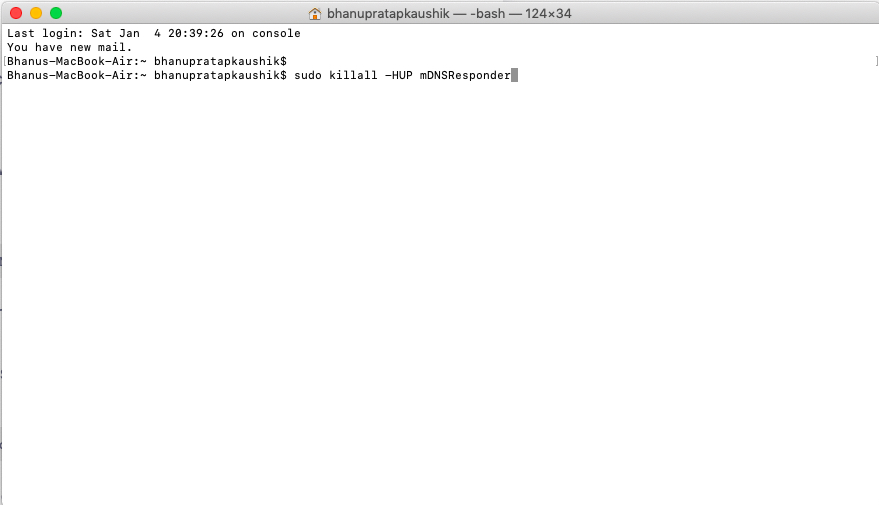
Step 2: Enter the following command to flush DNS cache if you are using Mac OS (Sierra, X El Capitan, X Mavericks, X Lion, or X Mountain Lion):
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
The command is different if you are using other versions of Mac OS X.
- For Mac OS X Yosemite, for example, you’ll need to enter the following command:
sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches
- For Mac OS X Snow Leopard, insert the following command:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
- For Mac OS X leopard, enter the command below:
sudo lookupd -flushcache
How to flush local DNS cache in LINUX systems?
By default, most Linux distributions do not cache local DNS records like Windows and Mac OS X. However, you can check the official Linux website to know whether your distribution has such local DNS caching.
There are however, ways to flush the DNS cache in Linux with a DNS service like nscd (name service caching daemon). Follow the steps below.
Step 1: Press Ctrl + Alt +T to open your terminal.
Step 2: Restart the nscd by executing the following command:
sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart
The command will clear DNS cache files in init.d subdirectory.
Wrapping Up
Most computer operating systems use DNS caching to store DNS information about every website you visit. While this is good in boosting network performance, the problem comes in when you decide to move your domain, experience connection issues, or when you suspect that your private information is at risk. When this happens, you might be prompted to clear your local DNS cache from time to time.
As you can see, clearing the DNS cache is super easy. We hope that this article was helpful to you.




